Repeated Cross-Validation for cv.glmnet
rcv.glmnet.RdThis functions returns the best lambda of repeated glmnet::cv.glmnet()
calls.
rcv.glmnet( x, y, lambda = NULL, nrepcv = 100L, nfolds = 10L, ..., trace.it = interactive(), mc.cores = getOption("mc.cores", 1L) )
Arguments
| x |
|
|---|---|
| y | response as in |
| lambda |
|
| nrepcv |
|
| nfolds |
|
| ... | further arguments passed to |
| trace.it |
|
| mc.cores |
|
Value
An object of class rcv.glmnet that extends the cv.glmnet
class.
References
Jerome Friedman, Trevor Hastie, Robert Tibshirani (2010). Regularization Paths for Generalized Linear Models via Coordinate Descent. Journal of Statistical Software, 33(1), 1-22. URL https://www.jstatsoft.org/v33/i01/.
Noah Simon, Jerome Friedman, Trevor Hastie, Rob Tibshirani (2011). Regularization Paths for Cox's Proportional Hazards Model via Coordinate Descent. Journal of Statistical Software, 39(5), 1-13. URL https://www.jstatsoft.org/v39/i05/.
See also
Author
Sebastian Gibb
Examples
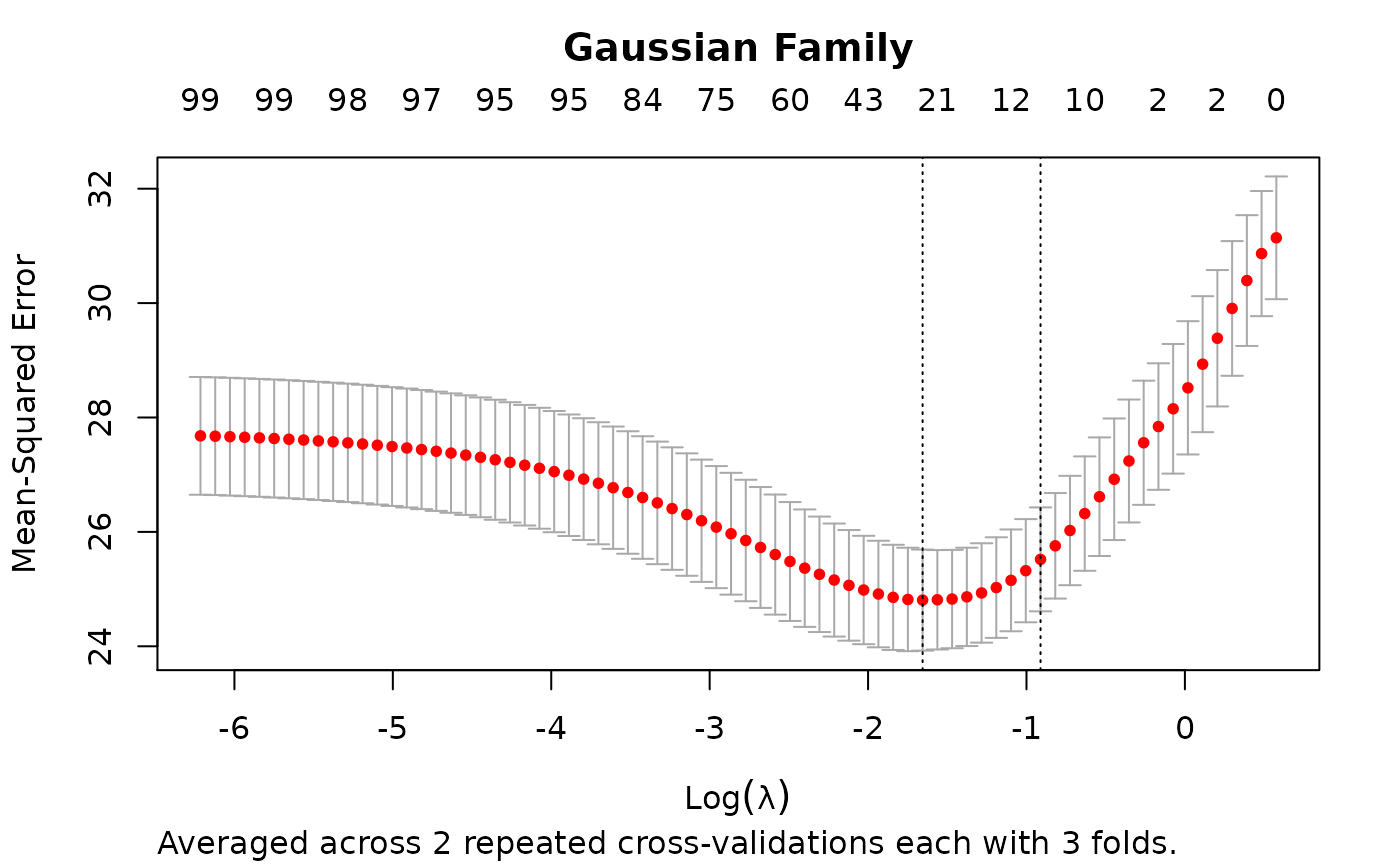
# Examples taken from ?"glmnet::cv.glmnet" set.seed(1010) n <- 1000 p <- 100 nzc <- trunc(p/10) x <- matrix(rnorm(n * p), n, p) beta <- rnorm(nzc) fx <- x[, seq(nzc)] %*% beta eps <- rnorm(n) * 5 y <- drop(fx + eps) set.seed(1011) # nrepcv should usually be higher but to keep the runtime of the example low # we choose 2 here rcvob <- rcv.glmnet(x, y, nrepcv = 2, nfolds = 3) plot(rcvob)#> 101 x 1 sparse Matrix of class "dgCMatrix" #> 1 #> (Intercept) -0.1162737 #> V1 -0.2171531 #> V2 0.3237422 #> V3 . #> V4 -0.2190339 #> V5 -0.1856601 #> V6 0.2530652 #> V7 0.1874832 #> V8 -1.3574323 #> V9 1.0162046 #> V10 0.1558299 #> V11 . #> V12 . #> V13 . #> V14 . #> V15 . #> V16 . #> V17 . #> V18 . #> V19 . #> V20 . #> V21 . #> V22 . #> V23 . #> V24 . #> V25 . #> V26 . #> V27 . #> V28 . #> V29 . #> V30 . #> V31 . #> V32 . #> V33 . #> V34 . #> V35 . #> V36 . #> V37 . #> V38 . #> V39 . #> V40 . #> V41 . #> V42 . #> V43 . #> V44 . #> V45 . #> V46 . #> V47 . #> V48 . #> V49 . #> V50 . #> V51 . #> V52 . #> V53 . #> V54 . #> V55 . #> V56 . #> V57 . #> V58 . #> V59 . #> V60 . #> V61 . #> V62 . #> V63 . #> V64 . #> V65 . #> V66 . #> V67 . #> V68 . #> V69 . #> V70 . #> V71 . #> V72 . #> V73 . #> V74 . #> V75 -0.1420966 #> V76 . #> V77 . #> V78 . #> V79 . #> V80 . #> V81 . #> V82 . #> V83 . #> V84 . #> V85 . #> V86 . #> V87 . #> V88 . #> V89 . #> V90 . #> V91 . #> V92 . #> V93 . #> V94 . #> V95 . #> V96 . #> V97 . #> V98 . #> V99 . #> V100 .#> 1 #> [1,] -1.3447658 #> [2,] 0.9443441 #> [3,] 0.6989746 #> [4,] 1.8698290 #> [5,] -4.7372693